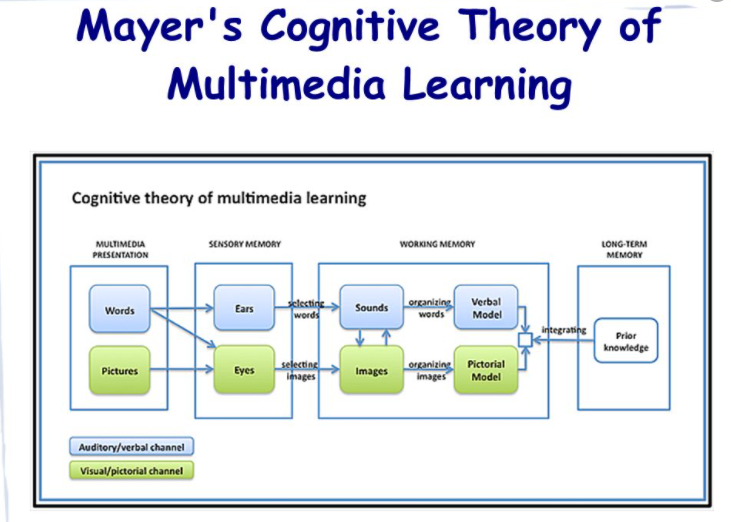
In modern society, students have more demands for scientific knowledge, and interdisciplinary learning is inevitable. Students need to accept more different concepts in a short time. Such fast and massive learning can be obtained on demand through multimedia. The existence of multimedia can also be used as supplementary materials, such as imaging informatics database, which can be used as an innovative reference for biomedical information and can also be used as learning materials. With the help of information, multimedia learning has become an indispensable tool for modern social learning. In the process of multimedia learning, students visualize and dynamic knowledge, interact with the acquired knowledge in time, and can also test the knowledge learned in time. Multimedia learning can reduce the knowledge gap between different students, promote conceptual understanding, and help students develop critical thinking.
Mentioned in Designing high-quality interactive multimedia learning modules by Huang, the development of multimedia modules includes five stages:
(1) understand the learning problem and the users’ needs;
(2) design the content to harness the enabling technologies;
(3) build multimedia materials with web style standards and human factors principles;
(4) user testing;
(5) evaluate and improve design.
Interactive multimedia learning materials combine various media, namely text, images, sound, video, animation and simulation, and students can control the way they use them. In addition, they can give feedback to students and allow students to actively participate in learning. Students use the given questions and work independently to identify knowledge concepts and understand knowledge principles. Since the process of problem solving requires critical thinking, critical thinking skills can be improved. This learning model is student-centered and can help students be more active, critical, creative, independent, and responsible in their learning.
Biblioghraphy:
References
Huang, C. (2005). Designing high-quality interactive multimedia learning modules. Computerized Medical Imaging And Graphics, 29(2-3), 223-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2004.09.017